Introduction: Why Garlic Needs a Different Packaging Approach
Garlic is a low-moisture but long-storage crop. It looks hardy, but incorrect packaging and storage quickly lead to:
Mold growth
Clove dehydration
Weight shrinkage
Yellowing or sprouting
Strong odor contamination
Export rejection
Unlike soft vegetables, garlic profit comes from curing quality, airflow control, and long-term storage discipline, not heavy protection. Proper packaging allows farmers to sell garlic months after harvest, often at much higher prices.
- Core Principles of Garlic Packaging
Garlic packaging must follow four rules:
Maximum ventilation
Zero moisture trapping
Light protection
Odor isolation
Any packaging that traps humidity or heat destroys garlic value faster than poor yield.
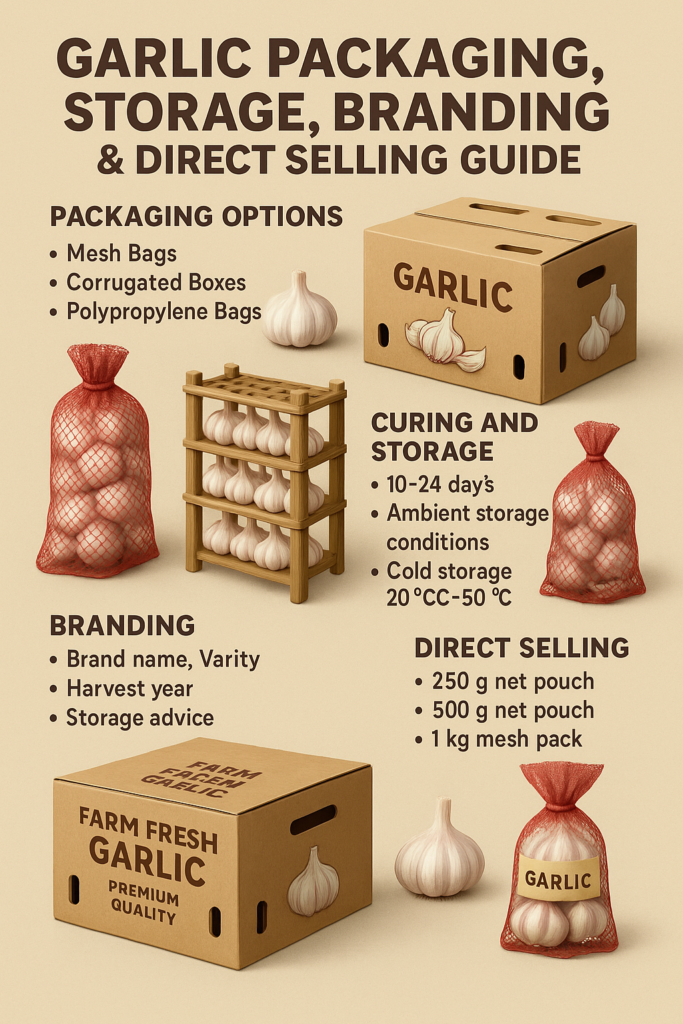
- Garlic Packaging Material System
3.1 Primary Contact Packaging (Clove Safety Layer)
Best materials:
Open mesh netting
Natural fiber net
Loose hanging bunches (traditional curing phase)
Avoid completely:
Plastic liners
Sealed poly bags
Non-ventilated sacks
Garlic skins act as natural protection; airflow is more important than cushioning.
3.2 Secondary Packaging (Main Holding Units)
A. Mesh Bags (Industry Standard)
Most widely used worldwide.
Common sizes:
1 kg
5 kg
10 kg
20 kg
25 kg
Benefits:
Excellent airflow
Easy inspection
Reduced fungal risk
Low-cost and reusable
Used for:
Wholesale
Storage
Export transport
B. Woven Polypropylene Bags (Only for Short Transport)
Used when:
Strong stacking is required
Transport duration is short
Limitation:
Less airflow than mesh
Must not be used for long storage
C. Corrugated Ventilated Boxes (Retail & Premium Markets)
Used for:
Supermarkets
Export retail
Direct-to-consumer sales
Specifications:
5-ply corrugated board
Side ventilation slots
Weight limits: 3 kg, 5 kg, 10 kg
Low-ink printing
- Garlic Grading System
Grading improves price and reduces storage loss.
Grade A – Premium Market & Export
Large uniform bulbs
Tight, dry outer skin
No sprouting
No mold spots
Grade B – General Retail
Medium bulbs
Slight size variation
Grade C – Processing
Small bulbs
Loose skin
Minor visual defects
Grading must be done after curing but before storage.
- Garlic Curing Process (Very Critical)
Curing determines garlic shelf life.
Curing Method
Duration: 10–20 days
Environment: Dry, shaded, well-ventilated
Method: Hanging bunches or thin layers on racks
Curing Objectives
Reduce moisture
Harden skins
Seal neck tissue
Prevent mold growth
Poor curing = guaranteed storage failure.
- Scientific Garlic Storage System
Garlic storage can be ambient or cold, based on market strategy.
Ambient Storage
Temperature: 20–25°C
Humidity: 60–70%
Strong airflow
Dark conditions
Cold Storage (Long-Term Strategy)
Temperature: 0–2°C
Humidity: 65–70%
Controlled ventilation
Cold storage is used for price timing and export control, not basic storage.
- Transport Guidelines
Garlic transport must avoid moisture and compression.
Rules:
Use ventilated vehicles
Keep produce dry at all times
Avoid rain exposure
Do not mix with high-moisture crops
Avoid plastic covers during transit
- Retail Display Standards
Retail garlic quality depends on dryness.
Display guidelines:
Open baskets or ventilated crates
No misting
Low-intensity lighting
Dry environment
Moisture exposure at retail immediately reduces shelf life.
- Branding Strategy for Garlic Farmers
Branding garlic is highly effective in retail and export markets.
Branding Elements
Clean brand name
Garlic variety (local / jumbo / export grade)
Net weight
Harvest year
Storage advice
QR code for traceability
Design Philosophy
Minimal
Natural colors
Low ink coverage
Clear text
Over-designed packaging increases mold risk.
- Direct Selling & Marketing Models
10.1 Retail Packs
250 g net pouch
500 g net pouch
1 kg mesh pack
10.2 Institutional Sales
Restaurants
Food processors
Pickle manufacturers
Packaging:
10–25 kg mesh bags
10.3 Export Selling
Uniform grading
Strong mesh bagging
Moisture records
Traceability labels
Export garlic packaging must strictly meet airflow standards.
- Packaging Cost Structure
Packaging TypeApprox Cost25 kg mesh bag₹15–2510 kg mesh bag₹8–121 kg net pouch₹2–45 kg corrugated box₹20–30
Packaging cost is low, but mistakes are expensive.
- Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Can garlic be stored in plastic bags?
No. Plastic causes moisture buildup and fungal growth.
Q2. Is cold storage necessary for garlic?
Only for long-term price-based selling.
Q3. Why is curing more important than packaging?
Without curing, no packaging will prevent spoilage.
Q4. Does branding really help in garlic sales?
Yes, especially in retail and export markets.
Q5. Can garlic be sold directly to consumers?
Yes, small net packs sell well in local and urban markets.
- Conclusion
Garlic packaging is not about heavy protection; it is about air, dryness and discipline. Farmers who invest time in proper curing, airflow-based packaging and scientific storage consistently outperform those who rush garlic to market. Branding further upgrades garlic from a bulk commodity to a traceable, retail-ready product. With the right post-harvest system, garlic becomes one of the safest and most profitable storage crops for farmers.
✍️Farming Writers Team
Love Farming Love Farmers
Read A Next Post 👇
Leave a ReplyShare your thoughts: We’d love to hear your farming ideas or experiences!