1. INTRODUCTION: WHY BEETROOT IS A HIGH-VALUE GLOBAL CROP
Beetroot (Beta vulgaris) is a rapidly expanding commercial vegetable crop grown in over 80+ countries. Known for its high nutritional value, medicinal benefits, juice industry demand, and strong export market, beetroot has become one of the fastest-growing root crops in global agriculture.
The crop is in demand among:
Juice industries
Salad and fresh markets
Retail chains
Hotels & catering services
Frozen vegetable processors
Exporters
Ready-to-cook food brands
Nutraceutical industries
Beetroot’s rising popularity is driven by its:
Anti-inflammatory properties
High iron and folate content
Natural red pigment (betanin)
Use in health drinks, detox beverages, powders
One-acre beetroot farming offers:
Extremely fast maturity (55–80 days)
Very high yield (10–16 tons per acre)
Strong year-round demand
Low risk & low maintenance
High-quality markets in multiple countries
Stable pricing
Beetroot suits both new farmers and established agribusiness professionals.
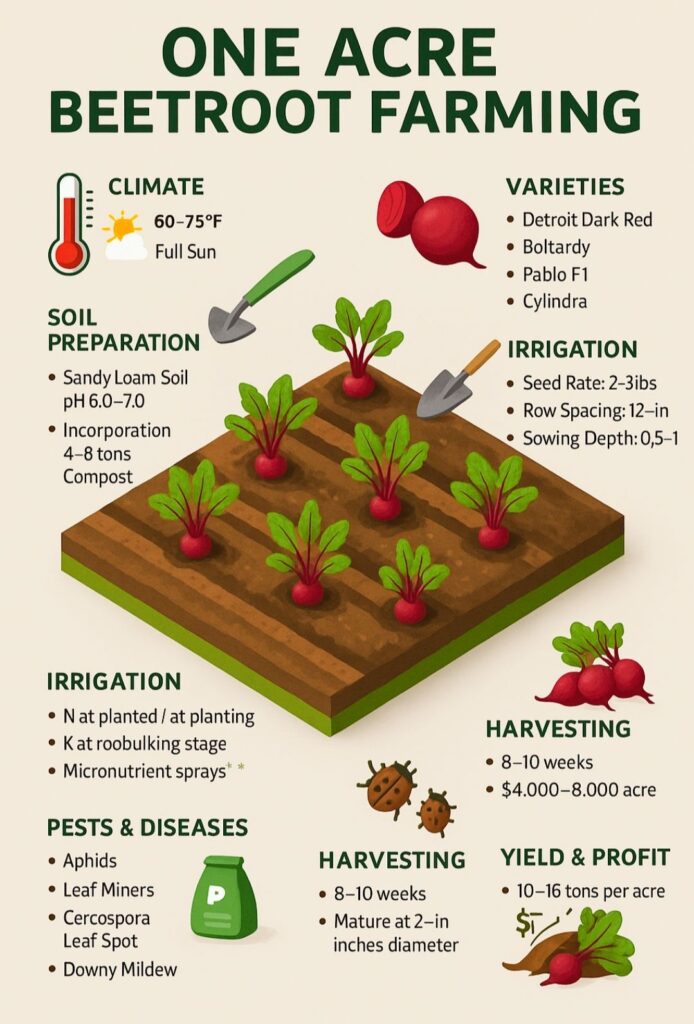
2. CLIMATE REQUIREMENTS
Beetroot is a cool-season root vegetable that thrives in the following conditions:
Temperature: 16–22°C
Minimum: 8°C
Maximum: 32°C
Sunlight: 6–8 hours
Humidity: 60–70%
Top Global Beetroot Producing Regions
USA (California, Wisconsin, Minnesota)
Europe (Germany, Poland, France, Netherlands, UK)
China
India (Punjab, Haryana, Karnataka)
Russia
Australia
South Africa
Kenya
It tolerates mild frost but cannot tolerate high heat.
3. SOIL REQUIREMENTS
Beetroot requires loose, deep, fertile soil for proper root expansion.
Ideal Soil
Sandy loam to loam
Soil pH: 6.0–7.0
Organic matter: Very High
Good drainage essential
Zero hardpan or stones
Soil Preparation Per Acre
1. Deep plough (2–3 times)
2. Remove all stones & clods
3. Add 4–6 tons compost/FYM
4. Add 50 kg neem cake
5. Create 3–4 ft wide raised beds
6. Fine tilth so roots become straight and uniform
Hard soil results in cracked, deformed roots — the biggest problem in beetroot farming.
4. SEED RATE, SEED TREATMENT & SOWING METHOD
Seed Rate per Acre
2–3 kg hybrid beetroot seeds
3–4 kg open-pollinated seeds
Seed Treatment
Soak 5–6 hours in water
Treat with Trichoderma
Shade-dry 30 minutes
Sowing Depth
1–1.5 cm (shallow sowing)
Germination Time
5–8 days (cool climate)
5. GLOBAL HYBRID VARIETIES OF BEETROOT
Popular International Hybrids
Detroit Dark Red
Ruby Queen
Crimson Globe
Red Ace
Pablo F1
Boltardy
Cylindra (long shape, high yield)
Chioggia (export premium)
Heat-Tolerant Varieties
Kestrel
Boro F1
Hybrid beetroot gives:
Uniform root size
Brighter red color
Higher sweetness
Longer shelf life
Higher yield
6. PLANTING LAYOUT AND SPACING
Ideal Spacing
Row-to-row: 1 ft (30 cm)
Plant-to-plant: 8–10 cm
Plant Population
80,000 – 1,00,000 plants per acre
Sowing Methods
Line sowing
Seed drill
Manual broadcasting (not recommended)
Proper spacing ensures round, uniform roots for fresh market & export.
7. IRRIGATION REQUIREMENT (DETAILED SCHEDULE)
Beetroot requires consistent soil moisture.
Week 1–2
Light irrigation daily
Helps germination
Week 3–5
Irrigate every 2–3 days
Week 6–9 (Root Bulking Stage)
Most critical phase
Irrigate every 2 days
Moisture stress leads to cracking
Week 10–12 (Maturity)
Irrigate every 4–5 days
Water Requirement (Drip)
350–500 liters per day per acre
Best Irrigation Method
Drip irrigation → helps in uniform root size, color, and weight.
8. FERTILIZER SCHEDULE (MONTH-BY-MONTH PROGRAM)
Basal Dose
FYM: 4–6 tons
Neem cake: 50 kg
NPK 10:26:26 → 40 kg
FERTIGATION PROGRAM
Month 1 (Vegetative Growth)
NPK 19:19:19 → 4 kg/week
Urea → 3 kg/week
Calcium nitrate → 3 kg/week
Month 2 (Root Development)
Potassium nitrate → 5 kg/week
Magnesium sulphate → 2 kg/week
SOP → 3 kg/week
Month 3 (Bulking & Maturity)
MKP 0:52:34 → 3 kg/week
Sulphur → 2 kg/week
Micronutrient Sprays
Every 20 days:
Boron 0.2% → prevents root cracking
Zinc 0.5%
Calcium chloride 0.5%
Beetroot is highly responsive to potassium and boron.
9. WEED MANAGEMENT
Weeds compete aggressively with beetroot seedlings.
Control Measures
Pendimethalin (pre-emergence)
Hand weeding (2–3 times)
Mulching with straw or plastic
Mulching boosts root size and improves color.
10. PEST MANAGEMENT
Major Pests
1. Aphids
Control: Imidacloprid
2. Leaf miner
Control: Cypermethrin
3. Cutworms
Control: Chlorpyrifos soil drench
4. Beet Armyworm
Control: Emamectin benzoate
11. DISEASE MANAGEMENT
1. Leaf Spot
Control: Mancozeb + Carbendazim
2. Downy Mildew
Control: Metalaxyl
3. Root Rot
Control: Trichoderma + soil drainage improvement
4. Cercospora Leaf Blight
Control: Copper oxychloride
Disease-free fields produce uniform red roots ideal for export.
12. THINNING (VERY IMPORTANT)
Thinning must be done 20–25 days after sowing:
Maintain 8–10 cm spacing
Essential for round, large roots
Poor thinning → small roots, uneven size.
13. HARVESTING TIMELINE
Beetroot matures in:
55–80 days (depending on climate)
Signs of maturity:
Root diameter: 5–7 cm
Deep red color
Leaves partially yellow
Harvest carefully to avoid bruising.
14. YIELD PER ACRE
Average Yield
10–12 tons per acre
Good Management
14–16 tons
Best Record
18+ tons per acre
15. GLOBAL MARKET PRICE (USD)
Region Price per kg
USA $0.50 – $1.20
Europe $0.70 – $1.50
Middle East $0.40 – $0.80
Asia $0.20 – $0.50
Africa $0.15 – $0.35
Processing Grade
$1.0 – $2.5 per kg
16. PROFIT PER ACRE (USD)
Revenue Example
14,000 kg × $0.40 = $5,600
Cost per Acre
$1,000 – $1,800
Net Profit
$4,000 – $8,000 per acre
Processing beetroot can raise profit 2–4×.
17. EXPORT MARKET OPPORTUNITY
Top importers:
UAE
Qatar
Saudi Arabia
Sri Lanka
Malaysia
Singapore
Maldives
Export Documents
Phytosanitary certificate
Invoice
Certificate of origin
IEC code
18. VALUE ADDITION BUSINESS (HIGH PROFIT)
Beetroot juice
Beetroot concentrate
Beetroot powder
Frozen beetroot
Roasted beetroot snacks
Dehydrated beetroot flakes
Value-added products yield 3–5× profit.
19. STORAGE & POST-HARVEST HANDLING
Storage Conditions
Temperature: 0–4°C
Humidity: 90–95%
Ventilated crates
Shelf Life
4–8 weeks
20. CONCLUSION
Beetroot is one of the fastest-maturing, most profitable and least risky one-acre crops. Its strong global demand, low production cost, suitability for juice and processing industries, and stable export markets make it ideal for youth farmers and commercial agripreneurs. With proper irrigation, fertilization, thinning and disease management, beetroot farming consistently delivers 10–16 tons yield and $4,000–$8,000 net profit per acre.
21. FAQ
1. What is the seed rate per acre?
2–3 kg hybrid seeds.
2. Beetroot grows in how many days?
55–80 days.
3. How much yield per acre?
10–16 tons.
4. Best irrigation for beetroot?
Drip irrigation.
5. What is the global price?
$0.20–$1.50 per kg.
6. What causes cracked beetroot roots?
Low moisture and boron deficiency.
7. Best beetroot hybrid?
Pablo F1, Detroit Red, Red Ace.
8. How to increase beetroot size?
Thinning, potassium, boron and regular irrigation.
9. Which countries import beetroot?
UAE, Qatar, Sri Lanka, Singapore.
10. Profit per acre?
$4,000–$8,000.
beetroot farming, one acre beetroot farming, beetroot yield per acre, beetroot cultivation guide, beetroot profit per acre
Beta vulgaris cultivation, root crop farming, beetroot pest control, beetroot disease management, vegetable agribusiness
Love farming Love Farmers
Read A Next Post 👇
https://farmingwriters.com/one-acre-cabbage-farming-complete-guide/
Leave a ReplyShare your thoughts: We’d love to hear your farming ideas or experiences!