1. Introduction: Why Tomato Is the World’s Most Profitable Vegetable Crop
Tomato is grown in more than 175 countries and is one of the most consumed vegetables worldwide. The global tomato industry exceeds $200 billion, driven by fresh consumption, sauce, puree, ketchup, dehydrated tomatoes, sun-dried products and processing industries.
Tomato farming is ideal for one acre because:
High yield potential
High global market demand
Multiple harvesting cycles
Year-round production in many climates
Fast maturity
Easy storage and transport
Extremely profitable with modern hybrid seeds
One acre of tomato, if managed properly, can become a stable, year-round income source for small and medium farmers.
2. Climate Requirements (Global Zone-Based Guide)
Tomato thrives in a wide range of climates:
Optimal Climate Conditions
Temperature: 20–30°C
Maximum tolerable: 35°C
Minimum: 10°C
Sunlight: 6–8 hours/day
Humidity: 50–70%
Top Global Tomato Regions
Americas: USA (California, Florida), Mexico, Brazil
Europe: Spain, Italy, Netherlands
Asia: India, China, Turkey
Middle East: Egypt, Saudi Arabia (greenhouse)
Africa: Kenya, Ethiopia, Nigeria
Tomato is so adaptable that it remains one of the top crops in protected as well as open-field farming.
3. Soil Requirements
Tomato thrives best in:
Sandy loam or loamy soil
Good drainage
Organic matter ≥ 2%
pH: 6.0–7.0
EC < 1 ds/m
Soil Preparation for One Acre
Deep ploughing
Add 8–10 tons of compost
Add 50 kg neem cake
Prepare raised beds (3 ft width, 1 ft height)
Install drip lines prior to transplanting
4. Seed Rate for One Acre Tomato Farming
Hybrid seeds: 10–15 grams
Open-pollinated seeds: 25–30 grams
Hybrid seeds produce 2–3x higher yield and are preferred globally.
Nursery Details
Use pro-trays
98 cavity trays
Cocopeat + vermiculite mix
Germination in 4–6 days
Seedlings ready in 22–25 days
5. Recommended Global Varieties (Open Field & Protected)
Open Field Hybrids
NS 516
Abhinav
US 440
Roma (processing)
Rio Grande (heat tolerance)
Protected / Greenhouse Hybrids
Anna F1
Arka Rakshak
Shanty
Kilele
Pusa Rohini
Processing Industry Varieties
Heinz 1350
UC82
Roma VF
Each region uses different hybrids based on climate and market.
6. One Acre Planting Layout (Correct Scientific Spacing)
Row spacing: 3 ft
Plant spacing: 1.5 ft
Plant Population per Acre
9,000 – 11,000 plants
Staking or trellising improves fruit quality and disease resistance.
7. Irrigation Requirement (Exact Water Schedule)
Tomato is sensitive to water stress.
Daily Requirement
Initial stage: 1 liter/plant/day
Flowering stage: 1.5–2 liters
Fruiting stage: 2.5–3 liters
Maturity stage: 1.5 liters
Best Method: Drip Irrigation
Saves 35–45% water
Reduces disease
Supports fertigation
8. Fertilizer Schedule (Complete Month-by-Month Program)
Basal Dose (Before Transplanting)
Farmyard manure: 8–10 tons
NPK (12:32:16): 50 kg
Neem cake: 50 kg
Fertigation Schedule
Week 1–4 (Establishment stage)
NPK 19:19:19 → 4 kg/week
Calcium nitrate → 2 kg/week
Week 5–8 (Flowering stage)
NPK 13:00:45 → 5 kg/week
Magnesium sulphate → 3 kg/week
Week 9–14 (Fruit development)
Potassium nitrate → 6–7 kg/week
Calcium nitrate → 3 kg/week
Week 15 onwards (Ripening stage)
Mono Potassium Phosphate → 3 kg/week
Micronutrients (Spray)
Boron 0.2%
Zinc 0.5%
Calcium chloride 0.2%
9. Pest & Disease Management (Global Standard)
Major Pests
1. Fruit Borer
Control: Emamectin Benzoate 5 SG
2. Whiteflies
Control: Imidacloprid
Also controls virus transmission
3. Thrips
Control: Spinosad
4. Aphids
Control: Neem oil 3% or Thiamethoxam
Major Diseases
1. Early Blight
Control: Mancozeb + Carbendazim
2. Late Blight
Control: Metalaxyl or Cymoxanil
3. Powdery Mildew
Control: Wettable sulphur
4. Bacterial Wilt
Control: Soil drenching with streptocycline + copper oxychloride
5. Leaf Curl Virus
Control: Whitefly control + resistant hybrids
10. Yield Estimation (One Acre)
Properly managed one acre tomato farm yields:
25–35 tons (25,000–35,000 kg) open field
40–60 tons protected farming
11. Market Prices (Global USD Pricing)
Market Price per kg (USD)
USA $0.80 – $1.50
Europe $1.00 – $2.00
Middle East $0.70 – $1.20
Africa $0.40 – $0.80
India $0.25 – $0.70
Processed tomato products have even higher margins.
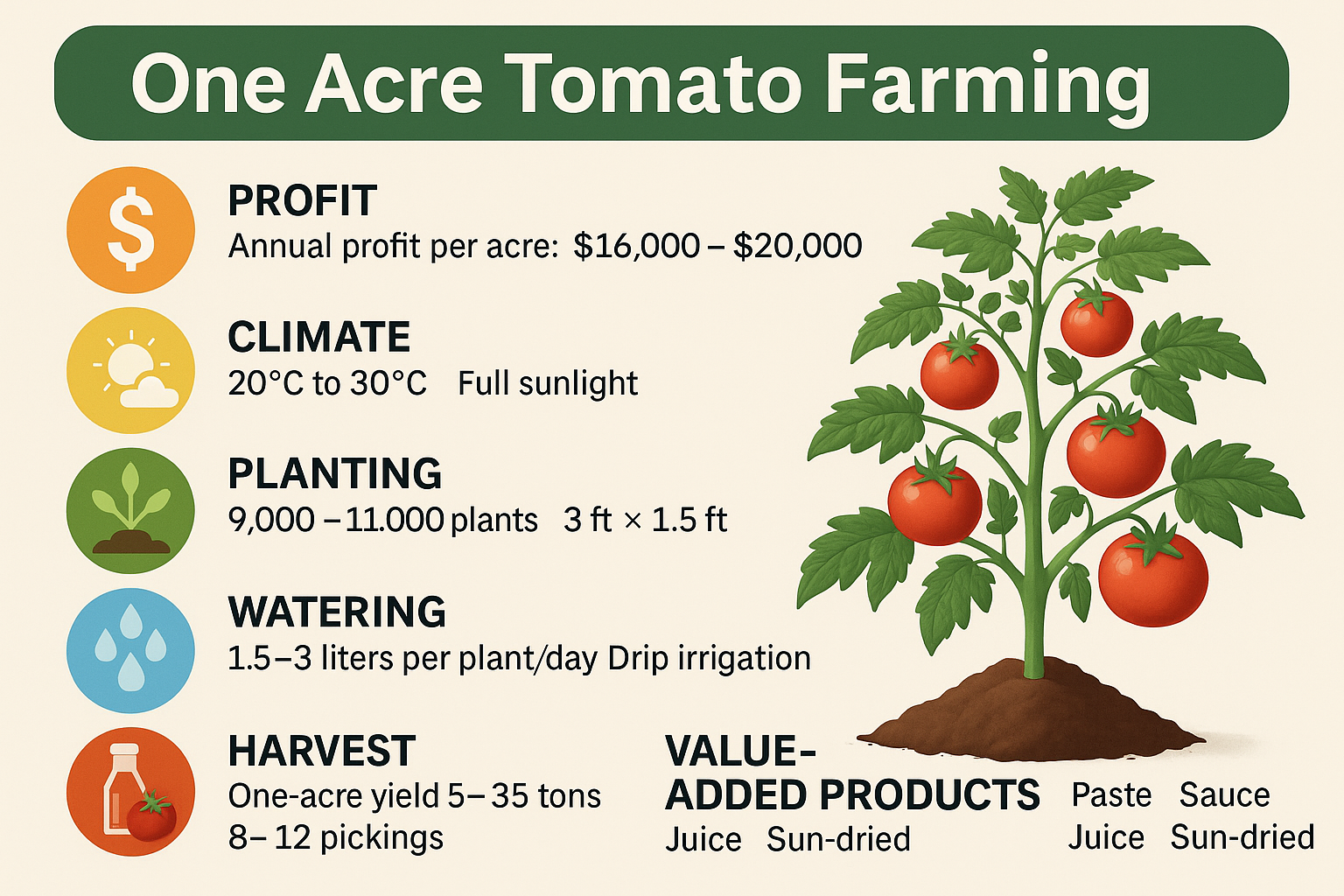
12. Profit Calculation (One Acre)
Revenue
Example:
30,000 kg × $0.80 = $24,000
Total Cost
Seeds, fertilizers, staking, irrigation, labor = $4,000 – $6,000
Net Profit
$16,000 – $20,000 per acre
Greenhouse tomato can reach $30,000+ per acre.
13. Post-Harvest Handling
Sorting
Grading
Washing
Waxing
Packing (5–10 kg crates)
Storage: 10–12°C
Good post-harvest handling increases shelf life.
14. Global Marketing Channels
Local Fresh Markets
Supermarkets
Vegetable vendors
Processing Industries
Ketchup manufacturers
Juice factories
Puree companies
Export Markets
Countries importing tomatoes:
UAE
Saudi Arabia
Kuwait
Nepal
Sri Lanka
Export price higher than domestic.
15. Value Addition (2–4X Profit Increase)
Tomato paste
Tomato puree
Tomato powder
Sun-dried tomatoes
Tomato sauce
Ketchup
Value-added products sell at 3–5× the fresh fruit price.
16. Government Subsidy & Loans
India
MIDH/NHB subsidy (40–50%)
NABARD horticulture loans
USA
USDA vegetable farming loans
Europe
CAP horticulture funds
Middle East
Greenhouse subsidies
17. Conclusion
One-acre tomato farming is one of the world’s most profitable vegetable farming systems. With modern seed varieties, drip irrigation, fertigation, and proper disease management, farmers can achieve high yields and stable income. Tomato farming supports both fresh and processing markets, providing long-term opportunities for new and experienced farmers.
18. FAQ (6 Questions)
1. How much profit can one acre tomato farming generate?
Average net profit globally is $16,000 – $20,000 per acre.
2. How many plants per acre?
9,000–11,000 plants.
3. Which irrigation method is best?
Drip irrigation with fertigation.
4. What is the seed rate?
10–15 grams hybrid seed per acre.
5. How many times can tomatoes be harvested?
8–12 pickings depending on hybrid.
6. Is tomato suitable for beginners?
Yes, if proper pest & disease control is followed.
Read A Next Post 👇
https://farmingwriters.com/one-acre-blueberry-farming-complete-guide/
✍️Farming Writers
Love farming Love farmers
Leave a ReplyShare your thoughts: We’d love to hear your farming ideas or experiences!