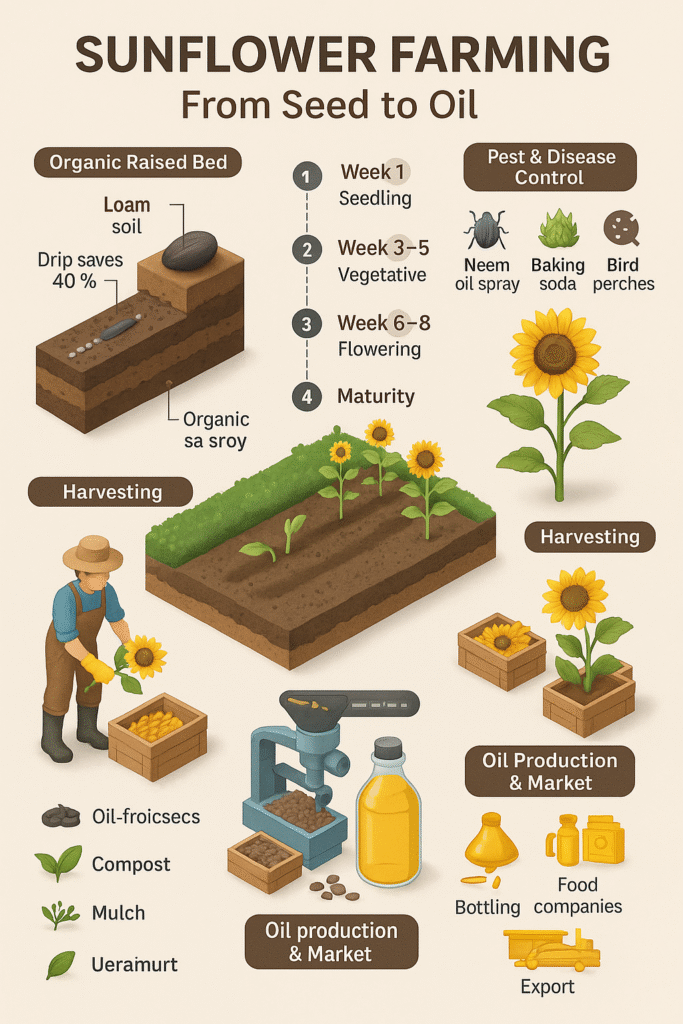
Introduction
Sunflowers (Helianthus annuus) are vibrant, high-value crops cultivated worldwide for both their aesthetic beauty and economic value. They are primarily grown for their seeds, which are used in the extraction of sunflower oil — a widely consumed, heart-healthy edible oil.
Sunflower farming is suitable for small-scale farmers as well as commercial agribusinesses due to its short growing cycle, low input cost, and multiple revenue streams.
History & Global Production Trends
Sunflowers originated in North America over 4,000 years ago and were first domesticated by Indigenous tribes for their oil-rich seeds. Today, they are grown extensively across Russia, Ukraine, Argentina, the United States, and India.
Top producers: Russia and Ukraine lead in sunflower oil exports.
Global trends: Due to increased demand for healthy oils and climate-resilient crops, sunflower cultivation is expanding in Africa and Asia.
Current innovations: High-oleic sunflower varieties and cold-pressed oil markets are trending worldwide.
Ideal Climate and Soil Conditions
Climate:
Sun-loving plant requiring full sun (6–8 hours/day)
Tolerates a wide range of temperatures (18°C to 35°C)
Grows best in dry, warm climates
Soil:
Well-drained sandy loam or loamy soil
pH between 6.0–7.5
Avoid heavy clay or waterlogged soils
Seed Selection & Varieties
Recommended High-Yield Varieties:
Sunbred 275 – Hybrid, high oil content
KBSH-44 – Popular commercial hybrid
PSH-996 – Resistant to downy mildew
DRSH-1 – Suitable for rainfed regions
Seed Rate:
2.5 to 3 kg per acre
Seed Treatment:
Treat seeds with Trichoderma or carbendazim to avoid fungal infection
Land Preparation & Planting
Deep plough the field and level it properly
Add FYM (farmyard manure) @ 10–15 tons per acre
Create ridges and furrows
Spacing: 60 x 30 cm
Depth: Sow seeds 3–5 cm deep
Best Sowing Time:
Kharif season: June–July
Rabi season: November–December
Irrigation Management
1st irrigation: Just after sowing
2nd & 3rd: At 30 and 60 days
Maintain moderate soil moisture
Avoid over-irrigation during flowering to prevent head rot
Organic Fertilization
NutrientOrganic SourceNitrogenVermicompost, cow dungPhosphorusRock phosphatePotassiumWood ash, banana compost
Foliar Spray: Jeevamrut or Panchagavya every 15–20 days
Intercropping with Sunflower
Sunflower is an excellent crop for intercropping due to its erect growth:
With pulses: Like moong, urad
With vegetables: Beans, okra
Benefits: Improved land utilization, weed suppression, better soil fertility
Pest & Disease Management
ProblemSymptomsOrganic SolutionCutwormsCutting of seedlingsNeem cake around baseDowny mildewWhite fungal growth under leavesTrichoderma spraySunflower Head MothHoles in flower headLight traps, neem oilAphidsSticky leaves, curlingSoap water + neem spray
Flowering, Harvesting & Yield
Flowering begins: 60–75 days after sowing
Harvest: When back of sunflower head turns yellow/brown & seeds harden
Cut heads with 15–20 cm stalk using sharp knife
Yield:
600–800 kg seeds per acre
Oil content: 35–45%
Sunflower Oil Extraction
Clean and dry harvested seeds
Use oil expeller or cold press machine
Filter and store oil in airtight containers
By-products: sunflower meal (cattle feed)
Sunflower-Based Products
Refined & Cold-Pressed Oil – Cooking & cosmetics
Roasted Sunflower Seeds – Healthy snack
Sunflower Meal – Protein-rich cattle feed
Biofuel – Used in biodiesel blending
Cosmetics – Face creams, oils, soaps
Organic Certification Process
To sell sunflower oil under “organic” label:
Register farm with certified organic agency (e.g., NPOP India, USDA)
Follow 3-year conversion from conventional to organic
Submit soil and product samples for lab testing
Maintain traceability records of inputs and harvest
Market & Business Opportunities
Raw seed sales to oil mills
Value-added products: roasted seeds, protein bars
Cold-pressed oil brands (small-scale startups)
Export opportunities to Europe, USA, Middle East
Profit Potential in Sunflower Farming
Input Cost (per acre)₹18,000–₹25,000Yield per acre600–800 kgAverage price/kg₹40–₹70Gross Income₹24,000–₹56,000Net Profit₹6,000–₹30,000
Sunflower for Home Gardeners
Ideal for terraces, balconies
Use 12-inch pots with loamy mix
6–8 hours of sunlight
Water when topsoil dries
Stake tall varieties
Export & Organic Certification
APEDA certification for export
EU/USDA organic label adds premium pricing
Target niche markets via e-commerce
Case Study: Farmer Success Story
Name: Shivpal Singh, Rajasthan
Switched to sunflower from cotton in 2021
Adopted intercropping with moong
Uses vermicompost and biofertilizers
Yielded 700 kg/acre and cold-pressed oil
Now sells 500 litres/month via Instagram at ₹600/litre
Result: Net income ₹3.5 lakh/year from just 5 acres
FAQs About Sunflower Farming
Q1. Can sunflowers grow in poor soil? Yes, they are tolerant but prefer loamy well-drained soils for best yield.
Q2. Is sunflower profitable compared to soybean? Yes, it requires less water and matures faster, making it a good alternative in dry zones.
Q3. How long do sunflowers take to mature? 90 to 110 days depending on variety.
Q4. Is organic sunflower oil more profitable? Yes, organic oil can fetch 2–3x higher price in urban and export markets.
Conclusion
Sunflower farming is a sustainable, high-value agribusiness model suited for farmers, startups, and organic growers. Its dual benefit of oil production and ornamental value makes it a profitable venture across various scales.
With the right seed selection, organic practices, and value addition, you can turn sunflowers into a golden opportunity.
✍️Farming Writers
Love farming Love farmers
Read A Next Post 👇
https://farmingwriters.com/gardenia-flower-farming-global-business/
Leave a ReplyShare your thoughts: We’d love to hear your farming ideas or experiences!