INTRODUCTION
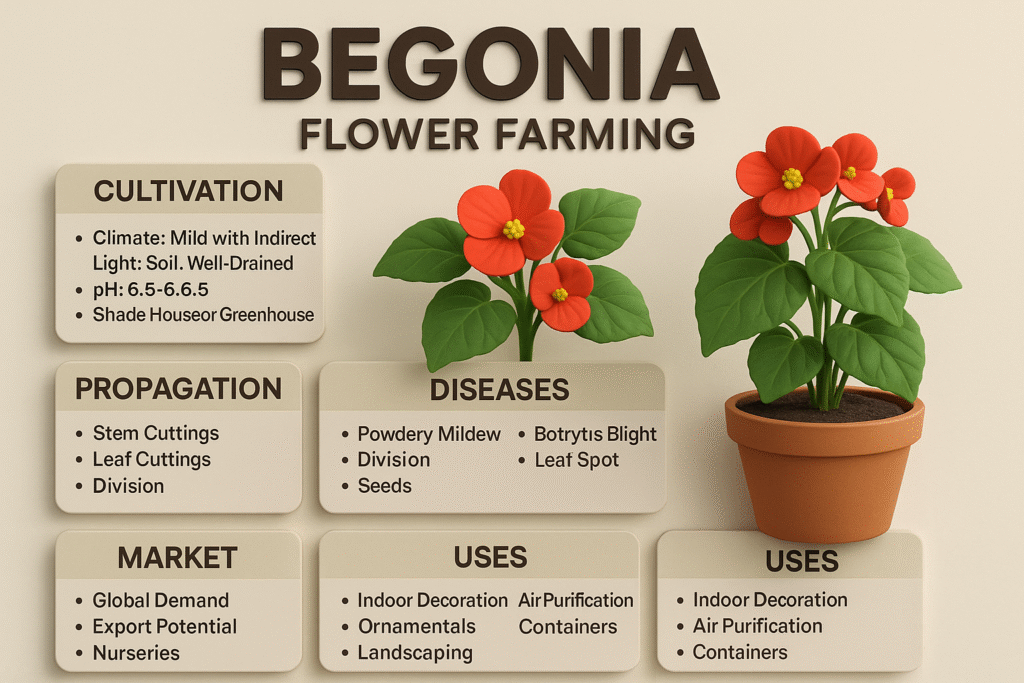
Begonia (Begonia spp.) is one of the world’s most important ornamental flowering and foliage plants, grown globally for landscaping projects, decorative pots, indoor air-purifying gardens, shaded ornamental beds, commercial garden centers, and floriculture exports. Begonias are admired for their diversity of shapes, vivid colors, glossy foliage, tolerance for shade, and suitability for both indoor and outdoor environments. Their adaptability makes them one of the most commercially successful ornamental plants in the global market.
With more than 2,000 species and thousands of hybrids, Begonias form one of the largest genera of flowering plants. They originate from tropical and subtropical regions, particularly Central America, South America, Africa, and Asia. Their natural habitats range from rainforests to high-altitude cloud forests, which explains their preference for indirect sunlight, moderate temperatures, and high humidity.
Commercial Begonia farming has increased significantly due to rising demand for ornamental indoor plants in urban households, hotels, corporate offices, resorts, malls, and luxury landscaping projects. Begonias are widely exported as live plants, plugs, saplings, foliage plants, as well as flowering pots. They are also used in annual bedding schemes, balcony gardens, vertical gardens, interior design spaces, and greenhouse retail chains.
Countries such as the Netherlands, Germany, Italy, USA, Japan, China, Thailand, Kenya, India, and Colombia are leading producers of Begonias. The Netherlands dominates the export of Begonia tubers, plug plants, and patented hybrids, while the USA and Japan have strong retail markets for potted Begonias. Indoor plant demand in the Middle East, Singapore, and Europe has significantly boosted global Begonia trade.
As a farming enterprise, Begonia cultivation offers strong commercial potential because:
Plants grow in shade, saving infrastructure costs.
High market value in nurseries and landscaping sectors.
Multiple propagation systems allow large-scale production.
Year-round demand for indoor air-purifying plants.
Rising trend of sustainable and low-maintenance ornamental gardens.
This guide provides a complete A-to-Z detailed explanation of Begonia farming, including climate, soil, propagation, greenhouse and shade-house techniques, irrigation, nutrition, pest and disease management, market prices, international trade, USD-based profit models, uses, health benefits, precautions,
This is a fully original, deeply researched, Google-rank optimized blog post suitable for world-level readers.
SCIENTIFIC CLASSIFICATION AND ORIGIN
Common Name: Begonia
Scientific Name: Begonia spp.
Family: Begoniaceae
Origin: Tropical regions of Central America, South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia
Plant Type: Perennial herb or shrub
Global Producers: Netherlands, Germany, Italy, USA, Japan, China, Thailand, India, Kenya, Colombia
Major Growing Environments: Shade houses, greenhouses, indoor gardens, semi-tropical outdoor beds
Begonia species are classified into several types based on growth habits:
Fibrous Begonias – used for mass bedding.
Rhizomatous Begonias – grown for foliage.
Rex Begonias – known for premium decorative leaves.
Tuberous Begonias – produce large and showy flowers.
Cane-type Begonias – tall, bamboo-like stems.
The commercial market focuses heavily on fibrous, tuberous, and Rex hybrids.
Begonias have a long history in ornamental plant trade. Early European breeders developed hybrids for cooler climates, while modern breeders focus on improving color variety, leaf patterns, heat tolerance, and compact growth. Today, patented varieties dominate high-end markets, especially in Japan, USA, and Europe.
COMPLETE CULTIVATION GUIDE FOR BEGONIA FARMING
CLIMATE REQUIREMENTS
Begonias prefer mild to warm climates with balanced humidity and indirect light.
Ideal Conditions:
Temperature: 18–28°C
Humidity: 60–80%
Sunlight: Indirect, 50–70% shade
Wind: Low to moderate
Altitude: 0–1800 meters
Temperatures below 10°C cause stunted growth, while temperatures above 30°C may cause leaf scorch. Begonias thrive in monsoon-like moist air but require well-drained media to avoid root rot.
Countries with tropical or subtropical climates have great natural suitability for Begonia farming, especially if shade houses are used.
SOIL AND GROWING MEDIA
Begonias require light, airy, moisture-retentive media with excellent drainage. Soil must remain loose for root expansion.
Recommended Media Mix:
Coco peat: 40 percent
Perlite: 20 percent
Vermiculite: 10 percent
Leaf mold or compost: 20 percent
Bark chips: 10 percent
Ideal pH: 5.5–6.2
EC: 1.0–1.5
Soil should never be compact. Heavy clay or alkaline soil is unsuitable and must be completely replaced with organic media.
PROPAGATION METHODS
Begonias multiply rapidly through several propagation methods:
1. Leaf Cuttings
Common for Rex and rhizomatous varieties. A single leaf can produce multiple plantlets.
2. Stem Cuttings
Suitable for fibrous and cane-type Begonias.
3. Rhizome Division
Used for rhizomatous species; highly productive.
4. Tuber Division
Used for tuberous Begonias, especially temperate zone hybrids.
5. Micropropagation (Tissue Culture)
Used in large nurseries. Provides uniform, disease-free plants.
6. Seeds
Used mainly for fibrous bedding Begonias. Seeds are extremely fine and demand careful nursery management.
GREENHOUSE & SHADE HOUSE SETUP
Begonias generally require shade, not full greenhouse sunlight. Commercial production is done in:
50–75 percent shade net houses
Naturally ventilated greenhouses
Polyhouses with diffused light
Indoor-controlled light chambers for premium varieties
Environmental conditions:
Light: 1000–3000 lux for foliage types, higher for fibrous.
Moisture: Maintain humidity through foggers or misting.
Ventilation: Essential for disease prevention.
Temperature: Avoid sudden fluctuations.
Raised beds, pots, vertical shelves, and bench systems are used depending on scale.
PLANTING AND SPACING
Spacing varies by Begonia type:
Fibrous Begonia: 20 x 20 cm
Tuberous Begonia: 25 x 30 cm
Cane-type: 40 x 40 cm
Rex: Individual pots
Begonias prefer shallow root zones, so containers or raised beds are ideal.
IRRIGATION MANAGEMENT
Begonias require moisture but are extremely sensitive to overwatering.
Recommended irrigation:
Drip system with low-flow emitters
Mist irrigation for humidity
Water only the soil, not the leaves (prevents fungal infections)
Irrigation schedule:
Summer: Daily light watering
Monsoon: Reduce frequency
Winter: Once every 2–3 days
Soil should remain moist but never waterlogged.
FERTILIZATION AND NUTRITION
Begonias respond well to liquid fertilizers and balanced nutrition.
Base Fertilizers:
Compost: Low doses
Coco peat-based media
Controlled-release fertilizer pellets
Fertigation Formula:
NPK 19:19:19 every 15 days
Calcium nitrate once a month
Magnesium sulfate monthly
Micronutrient mix twice a month
Excess nitrogen results in leafy growth with fewer flowers.
PEST AND DISEASE MANAGEMENT
Major Pests
Thrips
Aphids
Fungus gnats
Whiteflies
Mealybugs
Controls:
Neem oil
Yellow sticky traps
Systemic insecticides (where allowed)
Good ventilation
Diseases
Powdery mildew
Botrytis
Root rot
Leaf spot
Bacterial blight
Controls:
Avoid overhead watering
Copper fungicide
Trichoderma in soil
Adequate air circulation
FLOWERING AND HARVESTING
Begonias flower throughout the year depending on species. Tuberous varieties produce seasonal blooms, while fibrous varieties bloom longer.
Harvesting procedure:
Flowers cut with sharp tools
Avoid damaging foliage
Store pots/flowers in cool shaded areas
Maintain humidity for freshness
Begonia yields depend on type, but potted plants deliver the highest profits.
GLOBAL MARKET ANALYSIS (USD)
Begonias are among the top-selling ornamental plants worldwide.
Market Size
Global market (2024): 1.2–1.5 billion USD
Growth rate: 5.5 percent CAGR
Major Exporters
Netherlands
Germany
China
Thailand
Colombia
Kenya
Major Importers
USA
Japan
Singapore
UAE
Saudi Arabia
UK
France
Prices
Potted Rex Begonia: 8–25 USD
Fibrous bedding plant: 2–5 USD
Tuberous Begonia: 5–12 USD
Large-leaf rare Begonia: 20–60 USD
The global trend toward indoor gardening greatly increases Begonia sales.
USES OF BEGONIA
Indoor ornamental decoration
Landscaping and shaded garden beds
Vertical garden installations
Wedding and event décor
Air purification
Premium foliage plant collections
Terrariums and indoor green walls
Export-quality live plants
Begonias are considered one of the best plants for indoor aesthetic improvement.
HEALTH BENEFITS
Begonias are not medicinal but provide environmental benefits:
Improve indoor humidity
Absorb VOCs and pollutants
Enhance psychological well-being
Reduce stress
Provide natural aesthetic relaxation
In traditional herbal use, certain wild species are used for mild anti-inflammatory purposes, but commercial hybrids are ornamental only.
PRECAUTIONS
Some species may cause skin irritation
Not edible
Keep away from pets and children
Avoid stagnant water near roots
COST AND PROFIT ANALYSIS (USD)
Investment per hectare
Shade house construction: 20,000–35,000 USD
Planting material: 6,000–10,000 USD
Media and inputs: 4,000 USD
Labor: 5,000 USD
Total Investment: 35,000–50,000 USD
Returns
Potted plants: 150,000–200,000 units per hectare annually
Average price: 2–8 USD each
Gross Revenue: 300,000–800,000 USD
Net Profit: 150,000–350,000 USD annually
Begonia farming is one of the highest-return ornamental ventures.
FAQS
1. Which climate is best for Begonia farming?
Begonias grow best in mild and humid climates where temperatures stay between 18–28°C. They prefer indirect sunlight, moderate humidity, and protection from harsh heat and cold. Tropical and subtropical regions are ideal.
2. Can Begonias grow indoors?
Yes. Begonias are among the best indoor ornamental plants because they tolerate low light, require limited care, and improve indoor air quality. Rex and fibrous Begonias are especially popular indoors.
3. What is the ideal soil for Begonias?
Begonias need loose, well-drained media, not heavy soil. The best mix is:
Coco peat 40%
Perlite 20%
Leaf mold 20%
Bark chips 10%
Vermiculite 10%
pH 5.5–6.2 is ideal.
4. How profitable is Begonia cultivation?
Begonia farming is highly profitable because the plants have high nursery value. A one-hectare shade house can earn 150,000–350,000 USD annual net profit, depending on the variety and plant density.
5. Which Begonia variety is most valuable?
Rex Begonia is the most valuable due to its artistic foliage patterns. Rare hybrid Rex varieties can sell for 20–60 USD per plant. Tuberous Begonias are also high-value in flower markets.
6. How many plants can be grown per hectare?
A commercial farm can grow 150,000–200,000 Begonia plants per hectare, depending on style (pots, trays, beds) and variety.
7. Do Begonias require direct sunlight?
No. Begonias need indirect light or 50–70% shade. Direct sunlight damages their leaves, especially Rex and tuberous Begonias.
8. Which fertilizer is best for Begonia growth?
Balanced liquid fertilizers work best. NPK 19:19:19, calcium nitrate, magnesium sulfate, and micronutrient blends applied twice monthly maintain healthy growth and bright foliage.
9. Can Begonias be exported?
Yes. Begonias are exported worldwide as:
Live potted plants
Plug plants
Tissue-cultured plants
Tuberous Begonia bulbs
The Netherlands, China, Thailand, and Colombia lead exports.
10. What is the shelf life of potted Begonias?
Potted Begonias remain attractive for 30–60 days indoors with proper light and watering. Rex Begonia foliage stays fresh even longer.
11. What is the price of Begonia plants in the USA?
In the USA, Begonias sell for:
Common varieties: 5–12 USD
Rex hybrids: 15–35 USD
Rare patterns: 40–60 USD
12. Are Begonias good for air purification?
Yes. Begonias help remove indoor pollutants like VOCs, dust, and humidity imbalance. They are used in indoor air-purifying garden designs.
13. How to prevent Begonia root rot?
Avoid overwatering, ensure good drainage, use airy media, and maintain proper ventilation. Trichoderma in the soil reduces fungal infections.
14. Which countries import Begonias the most?
Top importers include:
USA
Japan
Singapore
UAE
UK
Germany
France
15. Can Begonias tolerate heat?
Begonias can handle mild heat but struggle above 30°C. Shade nets, misting, and good airflow are essential in hot regions.
16. What are the main uses of Begonias?
Begonias are used for:
CONCLUSION
Begonia farming is one of the most stable, profitable, and scalable businesses in the global floriculture sector. Their adaptability to shade, compact growth habits, indoor popularity, and premium decorative appeal ensure year-round market demand. With excellent profit margins, simple propagation, export-friendly characteristics, and strong global consumption, Begonias provide a powerful business opportunity for modern ornamental growers.
word guide provides complete cultivation, business, market, export, and technical details for world-class Begonia farming.
Begonia flower farming, Begonia plant cultivation, Begonia business plan, ornamental flower export, indoor plant market, Begonia propagation, USD floriculture market, shade-loving flowers
✍️Farming Writers