1. INTRODUCTION (GLOBAL OVERVIEW)
Garlic (Allium sativum) is one of the most ancient, powerful, and commercially valuable vegetables in the world. Cultivated in more than 120+ countries, garlic is a premium high-value crop used in:
Culinary industries
Medicine
Nutraceuticals
Pickles, sauces, chutneys
Dehydrated & processed garlic
Export markets (fresh + dried + powder)
Garlic has extremely strong market demand worldwide due to its rich medicinal value, high flavor profile, long shelf life, and continuous consumption in households, restaurants, hotels, and food processing factories.
It is among the top 3 most profitable vegetables in the world because of:
High market price
Long storage time
Huge export demand
Low water requirement
Best for small + big farmers
Garlic is a guaranteed profit crop for global farmers.
2. BOTANICAL DETAILS
Scientific Name: Allium sativum
Family: Amaryllidaceae
Plant Type: Cool-season bulb vegetable
Origin: Central Asia & Mediterranean
Pollination: Vegetative (cloves are used as seeds)
Edible Part: Bulb
Chromosome: 2n = 16
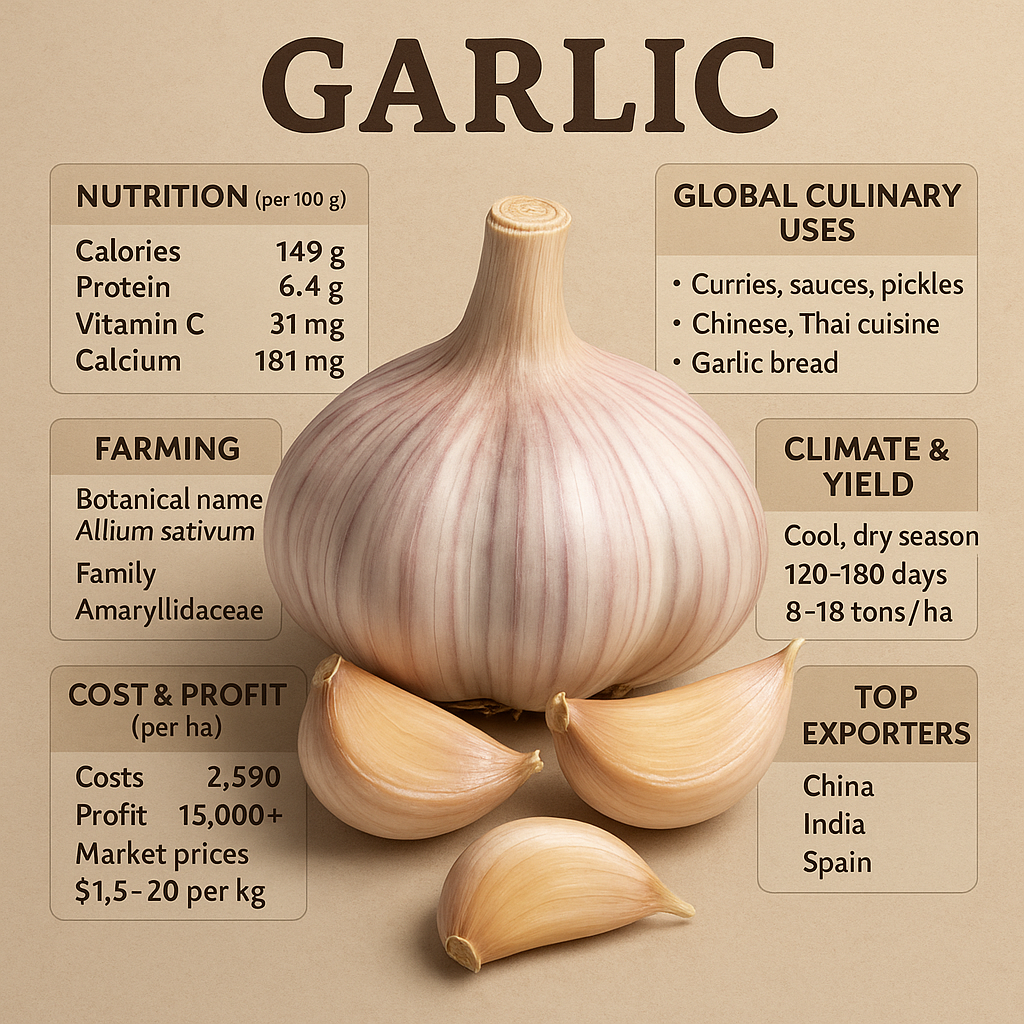
3. NUTRITION PROFILE (per 100 g fresh garlic)
NutrientAmountBenefitCalories149 kcalHigh energyProtein6.4 gHigh for vegetablesCarbohydrates33 gEnergy sourceFiber2.1 gDigestionVitamin C31 mgImmunityCalcium181 mgBonesIron1.7 mgRBC supportPotassium401 mgHeart healthAllicinHighAnti-bacterial, anti-viral
Garlic is one of the strongest natural antibiotics in the world.
4. GLOBAL CULINARY USES
Curries, soups, stir-fries
Sauces, chutneys, pickles
Garlic bread, pizza toppings
Chinese, Thai, Korean cuisine
Garlic powder, flakes, paste
Hotel, fast-food, restaurant chains
USA, Europe, Middle East, India, and China have the highest consumption.
5. SEED REQUIREMENT (CLOVES)
Per Acre
180–220 kg cloves
Per Hectare
450–600 kg cloves
Best seed garlic comes from China, India, Spain, Egypt.
6. SOIL REQUIREMENT
Sandy-loam soil
pH 6.0–7.5
High organic matter
Deep, well-drained
Soil rich in sulfur improves flavor
7. CLIMATE REQUIREMENT (COUNTRY-WISE)
India
Cool + dry climate
Best season: October–December
China
World’s largest garlic producer
Grows in cool spring & winter
USA
California is main garlic zone
Europe
Spain, Italy, France – mild winters, cool springs
Middle East
Grown in winter with irrigation
Garlic does not tolerate heavy frost or extreme heat during bulb formation.
8. IRRIGATION SCHEDULE
First irrigation after sowing
Next irrigation after 7 days
Then every 10–12 days
Reduce irrigation during bulb formation
Stop irrigation 10–15 days before harvest
Drip irrigation improves yield by 30–40%.
9. FERTILIZER SCHEDULE (GLOBAL STANDARD)
Basal Dose
FYM: 20 tons/ha
NPK: 80:40:60 kg/ha
Top Dressing
Nitrogen in 2–3 splits
Sulfur 25–30 kg/ha essential
Micronutrients: Zinc, Boron, Magnesium
Organic
Compost
Bone meal
Neem cake
Seaweed extract
10. PESTS & DISEASES
Pests
Thrips
Onion maggot
Nematodes
Diseases
Purple blotch
Stemphylium blight
White rot
Remedies
Neem oil
BT sprays
Copper fungicide
Crop rotation
Sulphur dusting
11. CROP DURATION (WORLDWIDE)
India: 140–160 days
China: 120–150 days
USA: 180 days
Europe: 150–180 days
12. GLOBAL YIELD DATA
Open field: 8–12 tons/ha
Hybrid varieties: 12–18 tons/ha
High-tech farming: 20+ tons/ha
13. COST OF CULTIVATION (USD ONLY)
ExpenseUSD per hectareSeed garlic$1,000Land prep$150Fertilizers$250Irrigation$120Labor$350Pesticides$130Mulching$200Harvesting + Packing$180Transport$90Miscellaneous$120Total Cost$2,590
Garlic has one of the highest seed costs, but gives huge returns.
14. GLOBAL PROFIT (USD ONLY)
Average Market Price
$1.5–3 per kg (fresh)
$4–8 per kg (dry high grade)
$10–20 per kg (powder/flakes export)
Example — Fresh Garlic Profit
Yield = 12,000 kg
Price = $2/kg
Revenue = $24,000
Profit = 24,000 – 2,590 = $21,410 per hectare
Example — Dry Garlic Profit
Yield dry equivalent = 4,000 kg
Price = $6/kg
Revenue = $24,000
Profit = 24,000 – 2,590 = $21,410
Example — Garlic Powder Export Profit
Yield = 1,000 kg powder
Price = $15/kg
Revenue = $15,000
Profit = 15,000 – 2,590 = $12,410
Garlic gives 10–20× return depending on market.
15. POST-HARVEST TECHNOLOGY
Drying in shade for 10–12 days
Remove roots & outer skin
Sort by bulb size
Store at 0–2°C
Shelf life: 6–7 months in cold storage
16. GLOBAL EXPORT MARKET
Top Exporters
China
India
Spain
Egypt
Argentina
Top Importers
USA
Brazil
UAE
Saudi Arabia
UK
Japan
Garlic has one of the strongest export markets in the world.
17. LOANS & INSURANCE
Loans
Crop production loans
Farm equipment loans
Cold storage loans
Drip irrigation loans
Insurance Covers
Pest attacks
Diseases
Drought
Excess rain
Market price crash
18. FAQ (15 QUESTIONS + GLOBAL ANSWERS)
1. How much seed garlic is needed per hectare?
450–600 kg.
2. What is garlic’s ideal climate?
Cool, dry climate; 12–25°C.
3. Is garlic profitable?
Yes, $15,000–$25,000 profit per hectare.
4. Can garlic grow in hot climate?
Only in winter or controlled farming.
5. Which fertilizers work best?
NPK + Sulfur + Zinc.
6. What is the maturity period?
120–180 days depending on region.
7. What are major pests?
Thrips and onion maggots.
8. Which country produces the most garlic?
China.
9. Which countries import garlic most?
USA, UAE, Brazil.
10. What is garlic export price?
$4–20 per kg depending on form.
11. Which variety is best?
G-282, G-1, Spanish Roja, California Early.
12. Can garlic be grown organically?
Yes, very successfully.
13. What irrigation method is best?
Drip.
14. What is garlic shelf life?
6–7 months in cold storage.
15. How to sell garlic at high price?
Grade, dry properly, target export, hotel supply.
19. CONCLUSION
Garlic is a world-class high-income crop suitable for all types of farmers. It has strong global demand, powerful nutritional and medicinal properties, and excellent export opportunities. With proper seed selection, climate management, fertilizer schedule, and post-harvest handling, farmers can earn 10–20 times profit consistently.
Garlic remains one of the safest, most profitable, and most stable vegetables in global agriculture.
✍️Farming Writers
Love farming Love farmers
