Snapdragon (Antirrhinum majus) is one of the most famous winter-season cut flowers admired globally for its tall spikes, dragon-shaped blooms, long vase life, and rich color varieties. Known as Dog Flower in India, and “Snapdragon” in Europe and the USA, this flower gets its name because pressing the sides of its blossom makes it look like a dragon opening its mouth.
Snapdragon is commercially cultivated across Netherlands, USA, Japan, Italy, Israel, Kenya, India, and China. It is a major flower in the cut-flower industry, especially in international flower auctions.
It comes in a wide color spectrum like pink, red, yellow, purple, white, orange, and bi-colors, making it a favorite for:
High-end bouquets
Wedding decorations
Church & festival décor
Floral arrangements
Indoor ornamental use
Apart from ornamental use, Snapdragon has applications in perfume, essential oil industry, dye extraction, and natural food coloring due to the presence of anthocyanin pigments.
Snapdragon is one of the most profitable winter-season exotic flowers because:
High demand in flower shops & premium florists
High vase-life of 7–14 days
Perfect for exports
Works well in greenhouse/polyhouse farming
Strong demand in weddings & events
Is blog me hum A to Z Snapdragon farming, soil, climate, seed propagation, greenhouse production, pest management, harvesting, global market, trade, uses, health benefits, FAQs, and USD profit model detail se cover karenge.
Scientific Classification & Origin
Common Name: Snapdragon / Dog Flower
Scientific Name: Antirrhinum majus
Family: Plantaginaceae
Origin: Mediterranean & Southern Europe
Plant Type: Annual/Biennial
Height: 30 cm – 120 cm
Top Producers: Netherlands, Kenya, USA, Japan, Italy, India
Snapdragon is native to the Mediterranean mountains, where it evolved as a hardy winter flower. Its commercial adoption began in Netherlands, the world leader in flower auctions.
Globally, Snapdragon is among the top 15 cut-flower varieties sold in floral markets due to its unique shape, color range, and premium appeal.
Snapdragon Flower Farming Guide
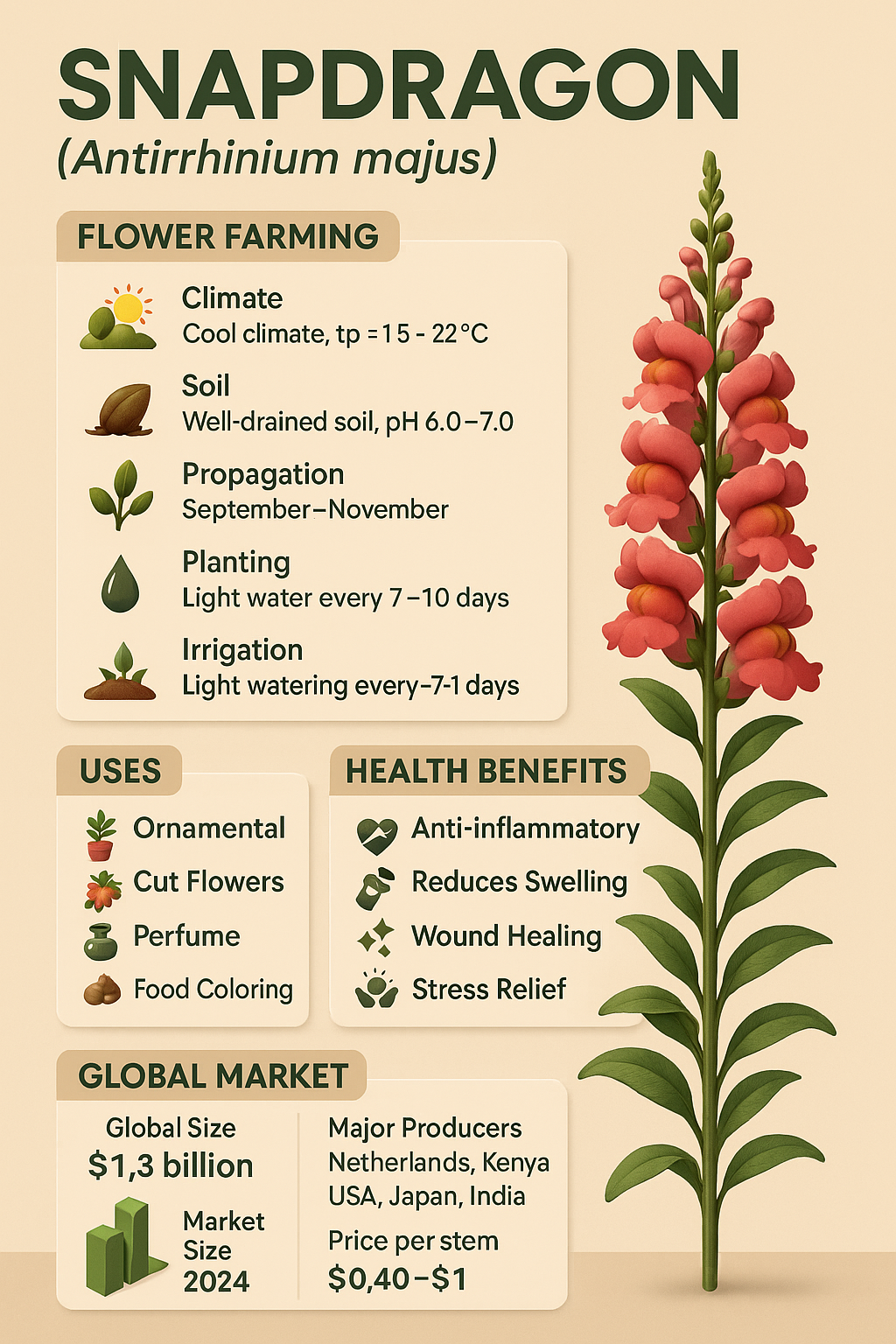
Climate Requirement
Snapdragon is a cool-season crop.
Best climate:
Temperature: 15–22°C
Humidity: 50–70%
Cannot tolerate high temperatures above 30°C
Prefers long-day and bright light
Best grown in:
Winter climates (India)
Greenhouses (tropical countries)
Soil Requirement
Well-drained sandy loam soil
pH 6.0–7.0
Soil rich in organic matter
Avoid heavy clay soils
Before planting, add:
Farmyard manure (FYM 15–20 tons/ha)
Neem cake 300–500 kg/ha
Propagation Methods
Snapdragon is propagated through seeds.
Seed germination temperature: 16–20°C
Germination time: 8–14 days
Transplanting after 30–35 days
Seeds are extremely fine — mix with sand for uniform sowing
Hybrid varieties are commercially used for export-quality flowers.
Planting & Spacing
Best planting time: September–November
Spacing:
20 × 30 cm (dwarf)
30 × 45 cm (tall varieties)
Plant density: 35,000–45,000 plants/ha
Irrigation
Light irrigation every 7–10 days
Drip irrigation is ideal
Avoid wet leaves to prevent fungal diseases
Fertilizer Schedule
Basal Dose:
FYM: 20 tons/ha
NPK: 60:40:40
Top Dressing:
Nitrogen every 25–30 days
Micronutrients: Boron, Calcium, Magnesium
Foliar sprays: 19:19:19 once every 15 days
Good nutrition boosts:
Spikes length
Number of florets
Color brightness
Pest & Disease Management
Common Pests:
Aphids
Thrips
Caterpillars
Whiteflies
Control:
Neem oil 2%
Sticky traps
Organic insecticidal soap
Diseases:
Damping off
Fusarium wilt
Powdery mildew
Rust
Stem rot
Control:
Trichoderma in soil
Copper fungicide
Proper ventilation
Flowering & Harvesting
Flowering
Begins in 70–90 days
Tall spikes harvested at ⅓ florets open stage
Best quality spikes: 60–90 cm
Harvesting
Harvest early morning
Cut stem at 45° angle
Immediately keep in preservative solution
Shelf Life
7–14 days (due to long-lasting spikes)
Excellent for export
Post-Harvest Handling
Grade by stem length and spike quality
Bundles of 10 or 20 stems
Cold storage at 2–4°C
Export in corrugated boxes
Global Market & Trade Analysis
Snapdragon is a high-value export flower.
Global Market Size (2024):
USD 1.3 billion
Major Exporters:
Netherlands
Kenya
Israel
Colombia
Japan
India (growing market)
Top Importers:
Germany
UK
UAE
USA
France
Singapore
Australia
Price Trends
Wholesale: $0.40–1 per stem
Retail: $2–4 per stem
Bouquets: $10–35 per bunch
Snapdragon is a preferred winter flower in Europe & the USA due to its:
Long vase life
Luxury appeal
Exotic shape
Netherlands Flower Auctions control 60% of global Snapdragon trade.
Uses of Snapdragon Flower
Ornamental Uses – gardens, landscapes, balconies
Cut Flowers – bouquets, wedding arches, arrangements
Perfume Industry – aromatic extracts used in perfumes
Food Coloring – anthocyanin-based natural pigment
Ayurveda & Herbal Uses – anti-inflammatory
Cosmetic Industry – used in creams and soaps
Health Benefits of Snapdragon
Anti-inflammatory
Reduces swelling
Used for healing minor skin wounds
Antioxidant
Stress-relief aroma
Improves mood
Traditional herbal medicine uses Snapdragon paste for skin cooling.
Precautions & Side Effects
Not edible
Sensitive skin may react
Avoid ingestion by pets
Use gloves while pruning
Cost & Profit Analysis (USD)
Investment per hectare
Land + preparation: $3,000
Seeds: $1,200
Fertilizer + irrigation: $1,500
Labor: $2,000
Total Cost: $7,000–8,500
Revenue
Production: 180,000–250,000 stems/ha
Selling price: $0.40–1 per stem
Total Revenue: $25,000–60,000
Net Profit
$18,000–45,000 per hectare annually
Snapdragon = Top 5 profitable winter cut flower crops.
FAQs
(Ready-to-publish):
How long does Snapdragon take to grow?
Which climate is best for Snapdragon farming?
Can Snapdragon grow in pots?
What is Snapdragon used for?
Is Snapdragon edible?
How much profit from Snapdragon farming?
How many stems per hectare?
How to increase stem length?
Which fertilizer is best for Snapdragon?
Can Snapdragon be grown organically?
What is Snapdragon’s vase life?
Which country exports Snapdragon the most?
How to control rust disease in Snapdragon?
Can Snapdragon grow in hot climate?
What is the spacing for Snapdragon plants?
Is Snapdragon good for bouquets?
How to store Snapdragon after harvest?
Can Snapdragon be exported?
Which Snapdragon variety is best for cut-flowers?
What is Snapdragon’s symbolic meaning? (Strength & grace)
Conclusion
Snapdragon farming is a high-profit floriculture business with strong global demand in the cut-flower, wedding, festival, and perfume industries. Its long, colorful spikes and long shelf life make it a premium flower in global flower auctions.
With proper winter farming or greenhouse systems, Snapdragon can yield excellent returns of $18,000–45,000 per hectare. This makes it one of the most profitable flowers after roses, gerberas, lilies, and carnations.
Snapdragon is not just a beautiful flower — it is a strong business opportunity for floriculture entrepreneurs in India and worldwide.
Snapdragon flower farming, Antirrhinum majus cultivation, Snapdragon market, Snapdragon uses, Snapdragon profits, greenhouse Snapdragon farming
✍️Farming Writers
Love farming Love farmers
Read A Next Post 👇
https://farmingwriters.com/gardenia-flower-farming-global-business/