1. Introduction: Why Potato Is One of the Most Profitable Global Crops
Potato is the 4th largest food crop in the world after rice, wheat and maize.
It is grown in 160+ countries and consumed daily across:
Homes
Hotels
Restaurants
Chips and snacks industries
French fries industry
Food processing companies
Export markets
Frozen food manufacturers
The global potato market exceeds $150 billion, making it one of the most stable, high-demand crops for commercial growers.
One acre of potatoes can produce:
10–14 tons average yield
Up to 18–22 tons high management yield
Potato farming provides a strong income, long-term storage stability, and high demand in every country year-round.
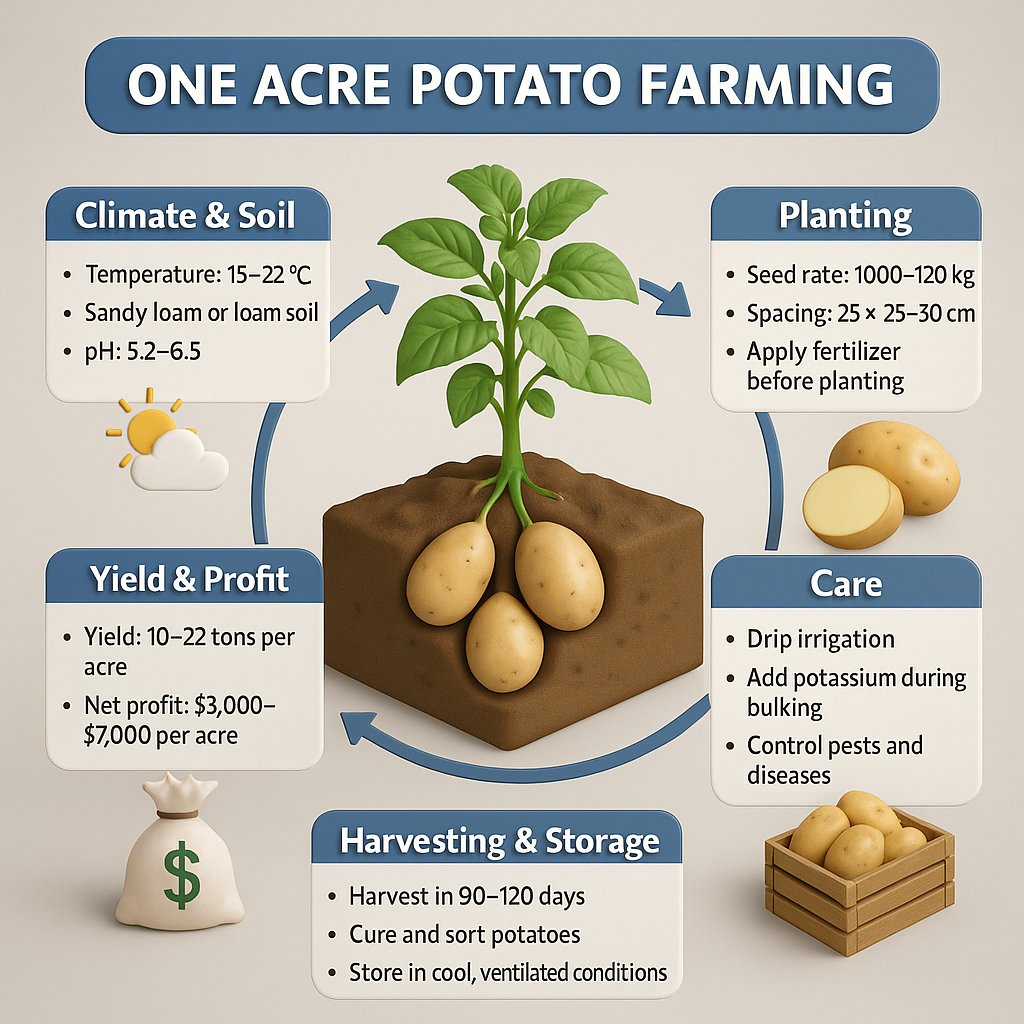
2. Climate Requirement (Global Growing Zones)
Potato prefers cool climates:
Best temperature: 15–22°C
Tubers stop growing above 30°C
Frost-free climate needed
Day length: 12–14 hours preferred
Global Potato Regions
USA (Idaho, Wisconsin, Washington)
Europe (Germany, Netherlands, France, UK)
China
India (Punjab, UP, Gujarat)
Russia
Canada
Bangladesh
Kenya
Peru (origin country)
Potato is very adaptable to many regions due to its short duration growth cycle.
3. Soil Requirements
Potato thrives in:
Sandy loam
Loam soil
Well-drained soil
Deep loose soil for tuber expansion
pH: 5.2–6.5
Avoid heavy clay or waterlogged soils.
Soil Preparation for One Acre
Deep ploughing
Add 8 tons compost
Add 50 kg neem cake
Prepare ridges and furrows at 2.5 ft spacing
Install drip irrigation (optional but best)
4. Seed Rate for One Acre (Exact Calculation)
Potato is planted using seed tubers.
Seed Requirement
10–12 quintals (1000–1200 kg) per acre
Seed size: 30–45 mm diameter
Disease-free certified seed required
Cut seed pieces only if tubers are large.
Seed Treatment
Fungicide dip (Mancozeb/Carbendazim)
Dry under shade
Apply Trichoderma powder
Good seed quality = high yield.
5. Recommended Global Potato Varieties
Table Potatoes (Fresh Market)
Kufri Pukhraj
Kufri Jyoti
Desiree
Atlantic
Yukon Gold
Russet Burbank
Processing Varieties (French Fries / Chips)
Lady Rosetta (LR)
Santana
Innovator
Frito-Lay varieties
Hermes
Early Maturity Varieties
Kufri Bahar
Kufri Khyati
Early Rose
6. Planting Layout for One Acre
Spacing
Row-to-row: 2.5 ft (75 cm)
Plant-to-plant: 10–12 inches (25–30 cm)
Plant Population
14,000–16,000 plants/acre
Planting depth: 3–4 inches.
7. Irrigation Requirement (Precise Water Schedule)
Potatoes require moisture but NOT standing water.
Drip Irrigation (Best Method)
First 20 days: 20–25 minutes daily
Tuber initiation (most critical): 30–40 minutes daily
Bulking stage: 40–50 minutes daily
Maturity: Reduce irrigation
Total Water Needed
400–600 liters per acre per day (approx.)
Excess water = rotting + disease.
8. Fertilizer Schedule (Month-by-Month Program)
Basal Dose (Before Planting)
FYM: 8 tons
NPK 12:32:16 → 50 kg
Neem cake → 50 kg
Fertigation Schedule
Early Growth (Week 1–4)
NPK 19:19:19 → 4 kg/week
Urea → 4 kg/week
Tuber Initiation (Week 5–6)
Potassium nitrate → 5 kg/week
Calcium nitrate → 2 kg/week
Bulking Stage (Week 7–10)
SOP (sulphate of potash) → 6 kg/week
Magnesium sulphate → 2 kg/week
Finishing (Week 11–12)
MKP 0:52:34 → 3 kg/week
Micronutrients
Spray every 20–25 days:
Boron → 0.2%
Zinc → 0.5%
Calcium → 0.5%
Correct nutrient management increases tuber size and market grade.
9. Earthing Up (Critical Operation)
Two times required:
First earthing: 25–30 days
Second earthing: 45–55 days
Earthing up prevents tubers from sun exposure and increases tuber weight.
10. Pest & Disease Management (Global Standard)
Major Pests
Aphids
Control: Imidacloprid
Cutworms
Control: Chlorpyrifos early soil drench
Potato Tuber Moth
Control: Pheromone traps + Spinosad
Major Diseases
Late Blight (Biggest threat)
Control: Metalaxyl, Mancozeb
Early Blight
Control: Copper oxychloride + Carbendazim
Black Scurf
Control: Seed treatment (Trichoderma)
Bacterial Wilt
Control: Resistant varieties + crop rotation
11. Harvesting Timeline
Potato matures in:
90–120 days depending on variety
Signs of maturity:
Plants dry from top
Skins firm and not easily peeled
Tubers uniform size
12. Yield Per Acre
Average yield
10–14 tons per acre
High yield (good management)
18–22 tons
13. Global Market Price (USD)
RegionPrice per kgUSA$0.30 – $0.70Europe$0.25 – $0.80Middle East$0.20 – $0.50Asia$0.15 – $0.40Africa$0.10 – $0.30
Processing potatoes (premium)
$0.50 – $1.00 per kg
14. Profit Calculation
Revenue
14,000 kg × $0.30 = $4,200
22,000 kg × $0.40 = $8,800
Cost Per Acre
$1,200–$2,000
Net Profit
$3,000–$7,000 per acre
Processing varieties may reach $8,000–$10,000 profit.
15. Storage (Important for Higher Profit)
Potato stores extremely well.
Storage Conditions
Temperature: 4°C
Humidity: 90–95%
Ventilated storage
Sprout inhibitors (Chlorpropham)
Farmers selling after 2–3 months earn 30–50% higher prices.
16. Export Guide
Top importing countries:
UAE
Malaysia
Qatar
Sri Lanka
Bangladesh
Oman
Required documents:
Phytosanitary certificate
Certificate of origin
Invoice
Packaging list
IEC code
17. Value Addition
Potato chips
French fries
Potato flakes
Dehydrated potato powder
Frozen potato products
Value-added products give 2–5× profit.
18. Conclusion
Potato is a global, stable, high-demand crop ideal for commercial farming on one acre. With correct seed selection, irrigation, fertilization, and disease management, potato farming can generate consistent income with strong market stability and excellent storage potential.
19. FAQ
1. How many kg of potato per acre?
10–22 tons.
2. How many kg seed required?
1000–1200 kg.
3. What is the profit?
$3,000–$7,000 (higher for processing varieties).
4. Which fertilizer is best?
Potassium-rich fertilizers during bulking stage.
5. When to harvest?
90–120 days.
6. Best irrigation method?
Drip irrigation.
✍️Read A Next Post 👇
https://farmingwriters.com/one-acre-ginger-farming-complete-guide/
✍️Farming Writers
Love farming Love farmers