Potato – Nutrition, Benefits, Farming, Cost, Profit and Global Market | Farming Writers
- Introduction
Potato (Solanum tuberosum) is one of the world’s most essential food crops, grown and consumed across every continent. Originating from South America, it has become a vital source of carbohydrates and nutrition for billions of people. Whether in India’s aloo sabzi, America’s fries, or Europe’s mashed potatoes, this humble tuber rules global kitchens.
Potato farming is one of the most profitable agricultural ventures due to its short growing cycle, high yield, and continuous market demand. It can be cultivated in diverse climates, making it a reliable crop for both small and large-scale farmers.
- Nutritional Value (per 100 g boiled potato)
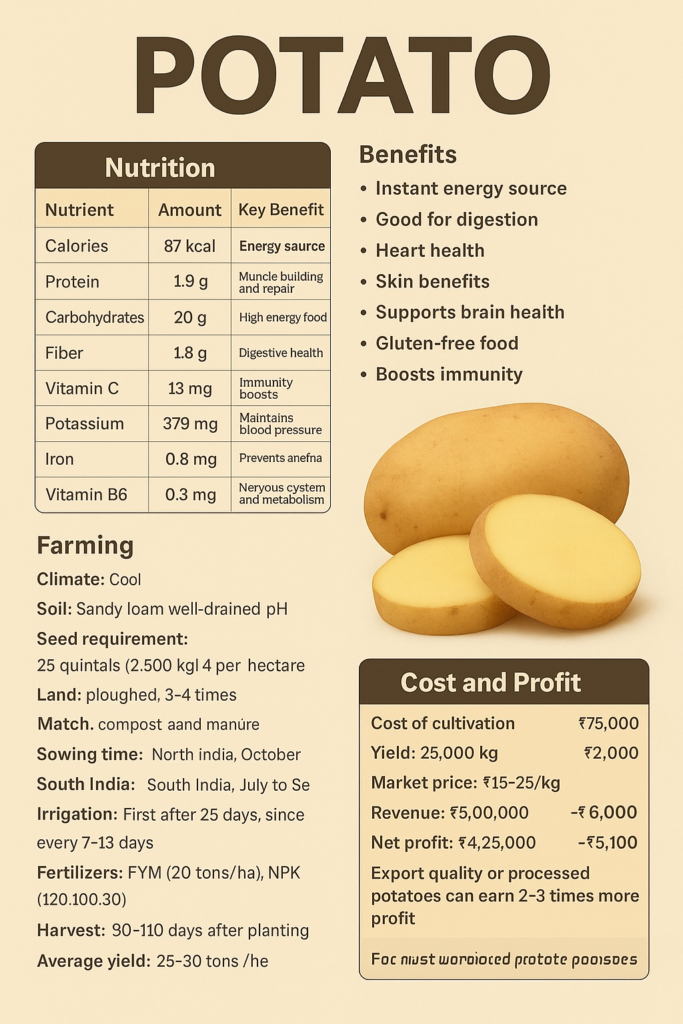
NutrientAmountKey BenefitCalories87 kcalEnergy sourceProtein1.9 gMuscle building and repairCarbohydrates20 gHigh energy foodFiber1.8 gDigestive healthVitamin C13 mgImmunity boosterPotassium379 mgMaintains blood pressureIron0.8 mgPrevents anemiaVitamin B60.3 mgNervous system and metabolism support
- Health Benefits of Potato
Instant energy source – Rich in complex carbohydrates for sustained energy.
Good for digestion – Fiber improves bowel movement and gut health.
Heart health – Potassium lowers blood pressure.
Skin benefits – Potato juice helps reduce dark spots and sunburn.
Supports brain health – Vitamin B6 supports nervous system function.
Gluten-free food – Safe for people with gluten intolerance.
Boosts immunity – Vitamin C and antioxidants protect against infections.
- Uses of Potato
Culinary Uses: Boiled, fried, baked, mashed, or processed into chips, snacks, or curries.
Industrial Uses: Potato starch in paper, textiles, adhesives, and alcohol production.
Medicinal Uses: Skin treatment, soothing burns, and natural facial packs.
- Cultivation Guide
Climate: Cool season crop; grows best between 15°C to 25°C.
Soil: Sandy loam soil, well-drained with pH 5.5–6.5.
Seed Requirement: 25 quintals (2,500 kg) per hectare.
Land Preparation: Plough 3–4 times; add compost and manure.
Sowing Time:
North India – October to December
South India – July to September
Irrigation: First irrigation after 25 days; then every 7–10 days.
Fertilizer: FYM (20 tons/ha) + NPK (120:100:80).
Harvest: 90–110 days after planting.
Average Yield: 25–30 tons per hectare.
- Cost and Profit Analysis (INR & USD)
Cost of Cultivation (per hectare):
ItemCost (₹)Cost (USD)Seed potatoes35,000$420Fertilizers & Manure10,000$120Labor12,000$145Irrigation6,000$72Transportation5,000$60Miscellaneous7,000$85Total Cost₹75,000$900
Yield and Revenue
Average Yield: 25,000 kg per hectare
Market Price: ₹15–25/kg (average ₹20/kg)
Revenue: ₹5,00,000 (~$6,000)
Net Profit:
₹5,00,000 – ₹75,000 = ₹4,25,000 (~$5,100) per hectare
Export quality or processed potatoes can earn 2–3 times more profit.
- Global Market Overview
Top Producers: China, India, Russia, USA, Ukraine
Export Leaders: Netherlands, France, Germany, Canada, USA
Import Markets: Africa, Middle East, Southeast Asia
Average Global Price: $1.2–2 per kg depending on quality and grade
Processing Demand: Frozen fries, chips, starch, alcohol industry
Potato is traded in over 150 countries, making it one of the top 5 global food crops after rice, wheat, maize, and soybeans.
- Marketing and Selling Strategies
Local Markets: Direct selling ensures stable income.
Contract Farming: Partner with food companies like McCain, Haldiram, ITC.
Cold Storage: Store potatoes and sell during high-price season.
Export: Target Middle East, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka for bulk exports.
Online Sale: Supply to e-commerce grocery chains (BigBasket, Blinkit, Amazon Fresh).
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the average yield of potato farming?
25–30 tons per hectare under normal conditions.
Q2. Is potato a good profit crop?
Yes, farmers can earn up to ₹4–5 lakh ($5,000–6,000) per hectare.
Q3. How long does it take to grow potatoes?
About 3–4 months from planting to harvest.
Q4. Can potato grow in hot regions?
It prefers cooler climates, but certain heat-tolerant varieties are available.
Q5. Which potato variety is best for chips and fries?
Kufri Chipsona, Kufri Jyoti, and Atlantic varieties are popular for processing.
- Conclusion
Potato is not just a kitchen staple but a high-value global crop. With its short cultivation period, minimal maintenance, and wide adaptability, it ensures consistent income for farmers.
From nutrition to profitability, potato stands as one of the most rewarding vegetables to grow. Whether sold fresh or processed, its market remains evergreen.
In conclusion: Potato offers excellent returns, supports food security, and continues to be one of the most traded and consumed vegetables in the world.
✍️Farming Writers
Read A Next Post
Leave a ReplyShare your thoughts: We’d love to hear your farming ideas or experiences!