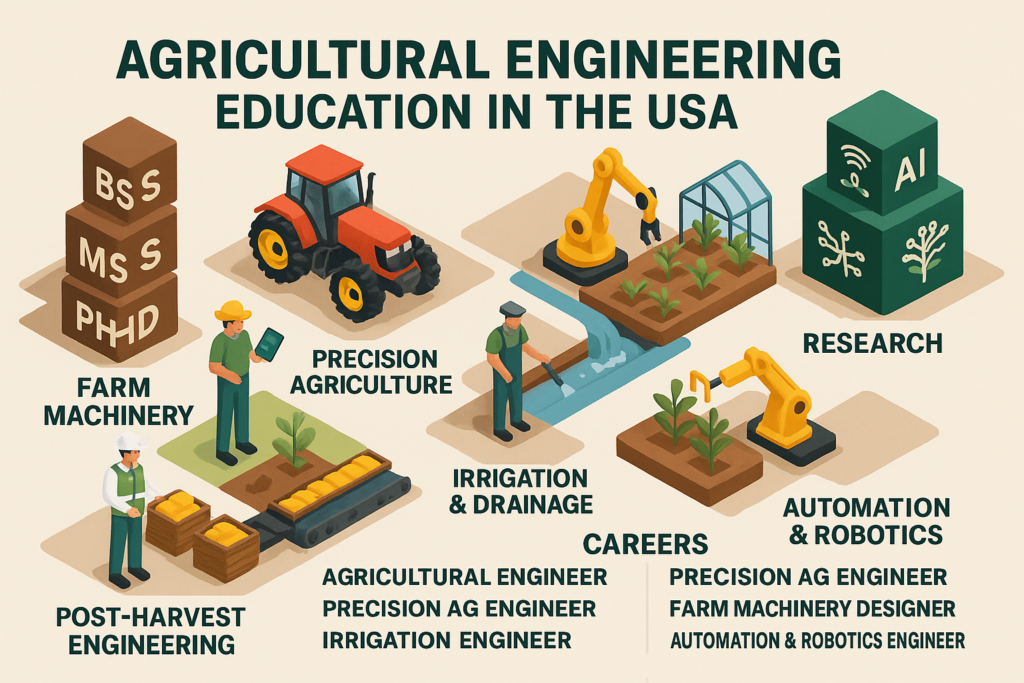
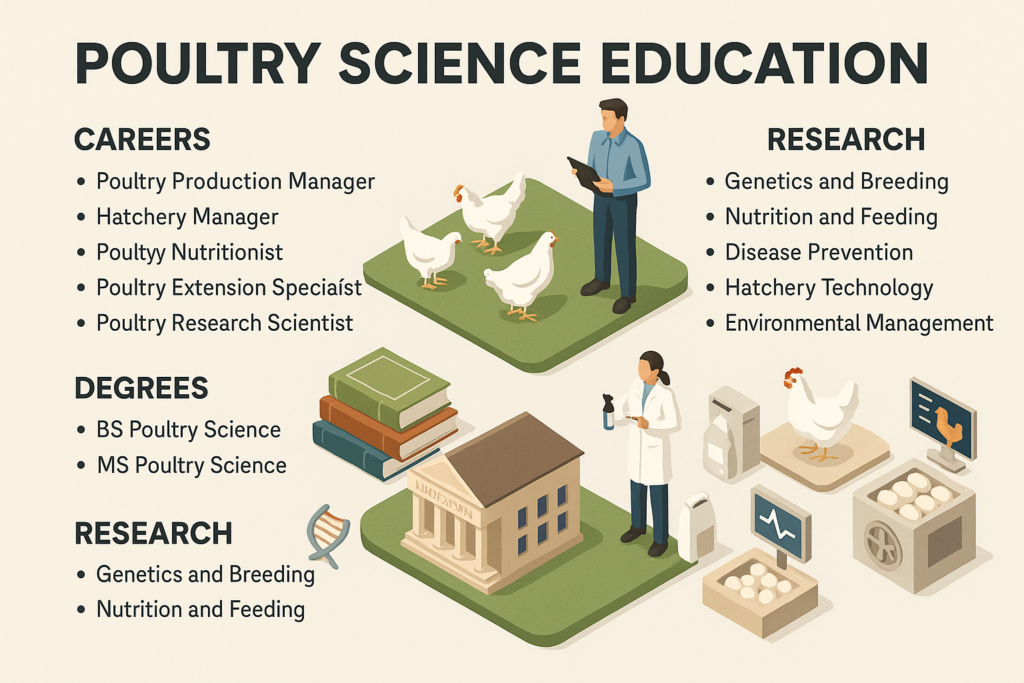
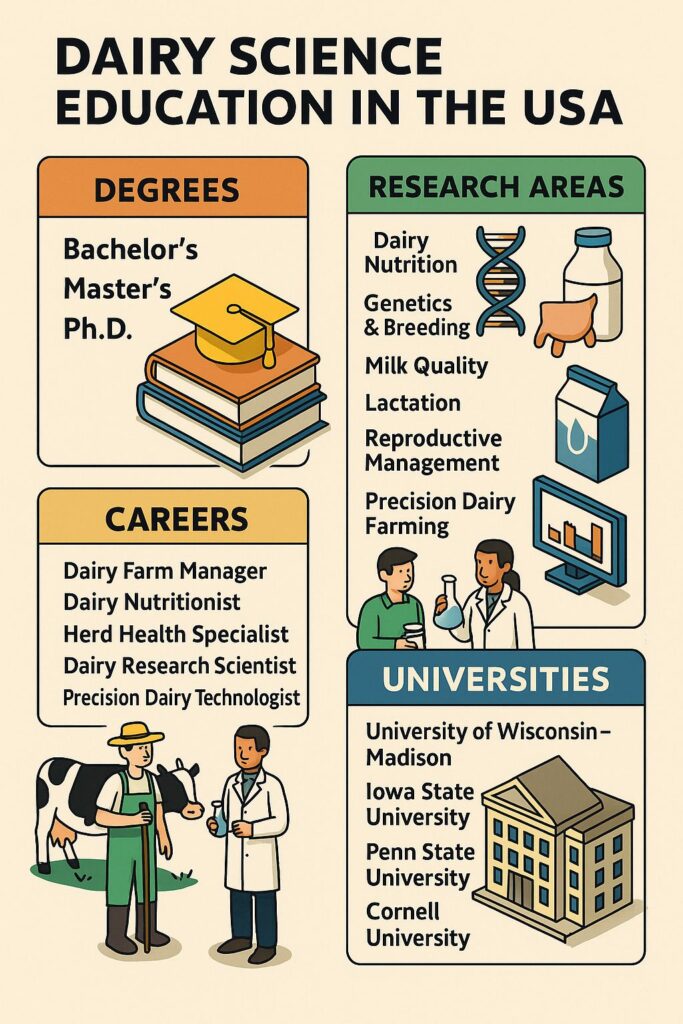
Horticulture education in the United States focuses on the scientific production note: fruits, vegetables, flowers, ornamental plants, nursery crops and landscape systems. Unlike general crop farming, horticulture deals with high-value crops, intensive management, post-harvest quality, and market-oriented production systems.
In the USA, horticulture is treated as a separate scientific discipline, supported by advanced laboratories, greenhouses, controlled-environment systems, plant breeding programs and strong industry collaboration.
- Scope of Horticulture Education in the USA
Horticulture education covers:
Fruit production (Pomology)
Vegetable production (Olericulture)
Floriculture (cut flowers, ornamentals)
Nursery management
Landscape horticulture
Greenhouse & protected cultivation
Urban horticulture
Post-harvest handling
Plant propagation
Tissue culture basics
Because horticulture crops generate high income per acre, this field attracts students interested in commercial farming, export markets and agribusiness.
- Degree Structure in Horticulture (USA)
Undergraduate Programs (BS Horticulture / BS Plant & Horticultural Sciences)
Core subjects include:
Principles of horticulture
Fruit crop production
Vegetable crop production
Floriculture and ornamental plants
Greenhouse management
Plant propagation
Nursery production systems
Soil & water management
Pest and disease management
Post-harvest physiology
Landscape design basics
Students spend significant time in:
Research orchards
Vegetable fields
Greenhouses
Shade houses
Nursery units
Graduate Programs (MS Horticulture)
Specializations include:
Fruit science
Vegetable science
Floriculture
Protected cultivation
Post-harvest technology
Plant growth regulators
Breeding of horticultural crops
Graduate students work on research trials, yield optimization, quality improvement and market-driven production systems.
Doctoral Programs (PhD Horticulture)
PhD research focuses on:
Genetic improvement of fruits & vegetables
Climate-resilient horticulture
Controlled-environment systems
Shelf-life enhancement
Precision horticulture
Urban & vertical farming
Sustainable ornamental production
- Top Universities for Horticulture in the USA
Leading horticulture universities include:
University of California, Davis
Cornell University
University of Florida (IFAS)
Michigan State University
North Carolina State University
Texas A&M University
Oregon State University
Washington State University
Purdue University
Ohio State University
These universities maintain:
Research orchards
Vegetable experiment stations
Climate-controlled greenhouses
Floriculture labs
Post-harvest research units
- Major Research Areas in US Horticulture
Fruit Science
Orchard systems
Pruning and training
Fruit quality improvement
Yield optimization
Vegetable Science
Intensive vegetable production
Protected cultivation
Drip irrigation integration
High-value crop systems
Floriculture
Cut flower production
Greenhouse ornamentals
Flower quality & longevity
Export-oriented production
Post-Harvest Technology
Storage systems
Cold chain management
Shelf-life extension
Quality retention
Protected Cultivation
Polyhouse systems
Hydroponics
Vertical farming
Climate control automation
- Careers After Horticulture Education
Graduates work in:
Commercial fruit farms
Vegetable production companies
Floriculture enterprises
Greenhouse operations
Nursery businesses
Export companies
Research institutions
Extension services
Urban farming startups
Job Roles
Horticulturist
Fruit production manager
Vegetable crop specialist
Greenhouse manager
Floriculture specialist
Nursery manager
Post-harvest consultant
Landscape horticulturist
Research scientist
- Salary Scope in the USA
Approximate earning patterns:
Greenhouse manager: stable to high
Nursery manager: moderate to high
Post-harvest specialist: high demand
Floriculture consultant: export-linked income
Research scientist: strong academic salary
Horticulture careers often offer higher per-acre income potential compared to field crops.
- Opportunities for International Students
International students prefer horticulture because:
High-value crop exposure
Advanced greenhouse systems
Export-oriented training
Research assistantships
Strong global applicability
Many graduates return to their home countries to start commercial horticulture businesses.
- Admission Requirements
Science background
Agriculture / biology degree (for MS/PhD)
TOEFL / IELTS
Statement of Purpose
Academic transcripts
- Why Horticulture Education in the USA Is Globally Respected
Strong research funding
Advanced infrastructure
Industry-linked education
Market-oriented focus
Climate-smart horticulture
FAQs (10)
Is horticulture different from agronomy?
Yes. Horticulture focuses on high-value crops, agronomy on field crops.
Is horticulture profitable in the USA?
Yes. It is one of the most profitable agriculture sectors.
Do horticulture students get greenhouse training?
Yes. Greenhouse work is compulsory.
Can international students study horticulture?
Yes, many programs accept international students.
Which university is best for fruit science?
UC Davis and Cornell University.
Is floriculture included in horticulture?
Yes, floriculture is a core specialization.
Are jobs available after horticulture?
Yes, in production, research, export and extension.
Is post-harvest part of horticulture?
Yes, it is a major component.
Does horticulture include hydroponics?
Yes, under protected cultivation.
Is horticulture future-proof?
Yes, due to rising demand for fruits, vegetables and flowers.
Conclusion
Horticulture education in the United States represents a high-value, science-driven and market-oriented agriculture pathway. With strong research backing, advanced greenhouse systems and global relevance, it offers excellent career and business opportunities for both domestic and international students.
✍️ Farming Writers Team
Love Farming Love Farmers
Read A Next Post 👇
https://farmingwriters.com/agricultural-extension-education-usa/